Science

Mrs Julie Hall and Mrs Alice Boyd are our science coordinators.

Intent
Our high-quality science curriculum provides the foundation for understanding the world. Science has changed our lives and is vital to the world’s future prosperity; all pupils should be taught essential aspects of the knowledge, methods, processes and uses of science. Our science curriculum aims progressively to build up a body of key foundational knowledge and concepts appropriate to age and stage of our pupils. Pupils are encouraged to recognise the power of rational explanation and dialogue and develop a sense of excitement and curiosity about natural phenomena. They are encouraged to understand how science may be used to explain occurrences, predict how things will behave, discuss and analyse causes. Children are encouraged to use enquiry and curiosity to question and test their ideas. At KSS we are developing and following an enquiry based science curriculum based around ‘big questions’ and practical, pupil led investigation around key concepts and ideas.
Our curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils:
- develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology, chemistry and physics
- develop understanding of the nature, processes and methods of science through different types of science enquiries that help them to answer scientific questions about the world around them
- are equipped with the scientific knowledge required to understand the uses and implications of science, today and for the future
Implementation
Science long term plan:
- Each year group will teach the areas of Science identified in the school’s long term plan to ensure coverage of statutory knowledge and skills.
- Each year group will teach all areas of Working Scientifically through planned investigative work, as identified in Year Group planning.
- The school’s Science progression of skills will be used to identify the learning objectives for each year group, in line with the school’s raised expectations.
Cross-curricular learning and real world contexts.
Wherever possible, a cross-curricular approach will be taken to the teaching of Science. Lessons will often be linked to children’s learning in English, Maths, Computing, Geography, PSHE etc.
Topic launch and land
Each half term topic will begin with a cross-curricular launch event to engage and motivate the children. This will also act as ‘knowledge harvest’ allowing teachers to assess children’s existing knowledge and skills in order to adapt planning and ensure appropriate levels of challenge for all children. Each half term will end with a land event which celebrates children’s learning and progress. This will involve the children communicating their learning in some way, for example exhibitions or assemblies.
Fieldwork
We understand, through analysis of relevant research, that fieldwork is an essential element of an outstanding Science curriculum and therefore ensure it is a high priority for all learners. Fieldwork is carried out in every year group across the school and the skills progression ensures children gradually build their fieldwork skills across the school.
Challenge and Support for all Learners
We understand that every learner develops differently and adapt our provision continuously to ensure every child receives the correct balance of support and challenge in order to achieve their very best. We recognise this fact and provide suitable learning opportunities for all children (including those who may be gifted and talented or have additional needs) by matching the challenge of the task to the ability of the child. Each child is valued, respected and challenged regardless of ability, race, gender, religion, social background, culture or disability.
Assessment
We use MAPP (Mapping attainment and progress for pupils) to assess children’s progress against the expectations of our INSPIRE curriculum. We assess children against both the requirements and standards of the National Curriculum as well as our school’s own raised expectations for all children. We assess them in working scientifically as well as their knowledge and understanding in each aspect of their study.
Scientific Knowledge and Conceptual Understanding
Spoken Language and Development of Higher-order Vocabulary Our scheme of work aims to develop scientific and conceptual understanding through a sequence of knowledge and concepts. However, we also believe that it is vitally important that our pupils develop secure understanding of each key block of knowledge, vocabulary and concepts in order to progress to the next stage. For this reason we are developing knowledge organisers to identify the key learning and Tier 3 vocabulary for each unit of work. These have been developed systematically across KS1 and KS2 collaboratively with the aim to avoid insecure, superficial understanding and will develop understanding of higher-order content. Pupils will be able to describe associated processes and key characteristics in common language but also be familiar with and use technical terminology (Tier 3) with accuracy. The knowledge organisers allow for a build up of extended specialist vocabulary. Our science curriculum is also planned to enable children to apply their mathematical knowledge to their understanding of science. In all key stages, children apply mathematical skills including collecting, sorting, presenting and analysing data.
The nature, processes and methods of science
‘Working scientifically’ specifies the understanding of the nature, processes and methods of science for each year group. It is not taught as a separate strand. Each unit of learning is planned to incorporate key features of scientific enquiry (such as observing over time, pattern seeking, identifying, classifying, grouping, comparative and fair testing, and researching using secondary sources). Pupils learn to use a variety of approaches to answer relevant scientific questions.
High-expectations
Our curriculum is designed with the national curriculum as a starting point but as we have extremely high expectations for our children so we have added additional challenge. These can be seen in the bold objectives in our INSPIRE curriculum. Although there is no requirement in the national curriculum, in order to give children an opportunity to begin to think how key concepts in forces and electricity affect our everyday life, we introduce our Key Stage 1 children to Forces within our Wheels, Wings and Wonderful Things topic in Year 1, and to Electricity with the Lighthouse Keeper’s Daughter topic in Year 2. In addition, we have used our Forest School, trips and outdoor environment to enrich our learning in science.
Science Topic Overviews:
This is the progression of science vocabulary that we teach our children. To support your child, you might like to look at the topic overviews and check your child knows the key vocabulary and the main ideas.
Please click on the images to enlarge the Knowledge Organisers.
Early Years
Science vocabulary and definitions
Early Years
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Everyday materials |
|
|
plastic |
a material that is light in weight and does not break easily. |
|
paper |
a material that comes from wood and is made into thin sheets |
|
wood |
the material that forms the trunks and branches of trees. |
|
metal |
a hard material such as iron, steel or gold |
|
float |
to rest on the surface of a liquid |
|
sink |
to go to the bottom |
|
hard |
not soft |
|
soft |
not rough or hard |
|
bendy |
an object that bends easily into a curved shape |
|
see-through |
allows you to see through it |
|
Electricity (adventures of the night) |
|
|
battery |
small device that that provide the power for electrical items like torches |
|
Sound (adventures of the night) |
|
|
loud |
making more noise |
|
quiet |
making little or no noise. |
|
Space (adventures of the night) |
|
|
night |
from sunset to sunrise |
|
day |
from sunrise to sunset |
|
dark |
the absence of light |
|
star |
a bright object that twinkles in the sky at night |
|
sun |
the star around which earth orbits |
|
Environment |
|
|
weather |
what the sky and the air outside is like, such as cold or sunny |
|
hot |
Something that is hot has a high temperature |
|
windy |
When the wind is blowing |
|
rain |
water that falls from the clouds in small drops |
|
winter |
the season between autumn and spring when the weather is usually cold |
|
autumn |
the season between summer and winter when the weather becomes colder and the leaves fall off tress |
|
summer |
the season between spring and autumn when the weather is warm or hot |
|
spring |
the season between winter and summer when the weather becomes warmer and the plants begin to grow |
|
Animals including humans (Marvellous me) |
|
|
grow |
increase in size |
|
baby |
a very young child |
|
child |
a human who is not 18 year old |
|
adult |
a human who is over 18 years old |
|
gill |
the organs on the side of a fish and other water creature through which they breathe |
|
sense |
these allow the body to see, smell, hear, taste, and touch |
|
touch |
to be aware of a person or object by being touched or touching |
|
taste |
the sensation of flavour in the mouth |
|
see |
to use the eyes to make out images |
|
hear |
to use the ears to make out noises |
|
Living things and their habitats |
|
|
jungle |
an area of lots of trees |
|
artic |
the areas near the north pole |
|
ocean |
an area which covers much of earth with salt water |
YEAR 1
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 1
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Materials (Everyday materials) |
|
|
material |
substance of which something is made of |
|
property |
is the word that describes what something is like |
|
use |
a purpose for or way in which something can be used |
|
rock |
the hard substance which the earth is made up of |
|
water |
clear liquid that has no colour, taste or smell |
|
fabric |
cloth or other material produced by weaving together cotton, wool or other threads |
|
shiny |
things that are bright and reflect light |
|
dull |
a colour or light that is not bright |
|
rigid |
firm and does not bend |
|
flexible |
capable of bending easily without breaking |
|
brittle |
hard but able to break easily |
|
waterproof |
does not let water pass through it |
|
absorbent |
material that soaks up liquid easily |
|
opaque |
if an object or substance is opaque, you cannot see through it |
|
transparent |
if an object is transparent, you cannot see through it |
|
rough |
uneven and not smooth |
|
smooth |
no roughness, lumps or holes |
|
elastic |
a rubber material that stretches when you pull it and returns to its original size and shape when you let it go |
|
Forces and Magnets (Pushes and Pulls) |
|
|
push |
when you push something, you use force to make it move away from you or away from its previous position |
|
pull |
when you pull something, you hold it firmly and use force in order to move it towards you or away from its previous position |
|
direction |
the path along with something moves |
|
force |
the pulling or pushing effect that something has on something else |
|
forwards |
is the direction ahead of you |
|
backwards |
is the direction behind you |
|
Seasonal Change |
|
|
hibernate |
animals that hibernate spend the winter in a state like a deep sleep |
|
migrate |
when animals move at a particular season from one part of the world to another |
|
temperature |
a measure of how hot or cold something is |
|
thermometer |
an instrument for measuring how hot or cold something is |
|
summer solstice |
is the day with the longest period of daylight |
|
winter solstice |
is the day with the shortest period of daylight and the longest night of the year |
|
season |
the main times of the year which can be divided and which have their own typical weather |
|
hail |
is a lump of ice that falls out of a storm cloud |
|
fog |
is mist which is very thick |
|
lightening |
is a powerful burst of electricity |
|
thunder |
the loud sound that follows a flash of lightening |
|
mist |
a mass or cloud of tiny water drops in the air |
|
Animals including humans |
|
|
amphibian |
is a class of animal. They live the first part of their lives in water and last part on the land |
|
bird |
a creature that has feathers, wings, lay eggs and are warm blooded |
|
fish |
a creature that lives only in water |
|
mammal |
an animal that breathes air, has a backbone and grows hair |
|
reptile |
an animal that has scales and lays eggs. They include animals like crocodiles, snakes, lizards and turtles |
|
structure |
is something of many parts that is put together |
|
omnivore |
person or animal eats all kinds of food, including both meat and plants |
|
herbivore |
an animal that only eats plants |
|
carnivore |
an animal that eats meat |
|
life cycle |
the series of changes that an animal or plant passes through from the beginning of its life until its death |
|
offspring |
a person’s children or an animal’s young |
|
reproduce |
to make more by having babies |
|
reproduction |
is the process by which a living organism creates a likeness of itself |
|
tadpole |
is a young frog that breathes and lives in water |
|
froglet |
is a young frog, one that has recently grown from a tadpole |
|
frogspawn |
is a soft substance like jelly which contains the eggs of a frog |
|
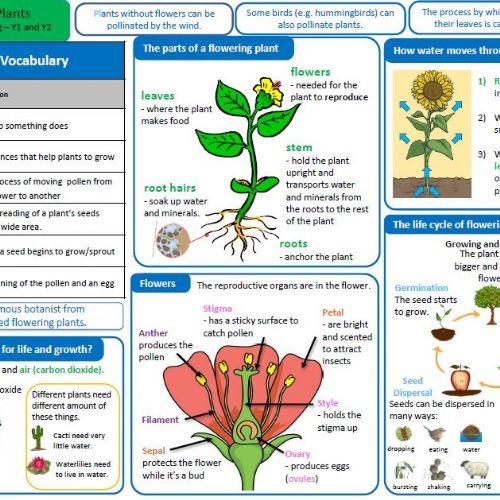
Plants |
|
|
blossom |
the flowers that appear on a tree before the fruit |
|
stem |
the thin, upright part of a plant on which the flowers and leaves grow |
|
leaf |
the part of a tree or plant that are flat, thin and usually green |
|
roots |
the parts of a plant that grow under the ground |
|
crown |
is the area above the trunk |
|
twig |
a very small thin branch that grows out from a main branch of a tree or bush |
|
trunk |
the main large stem from which the branches grow |
|
branches |
parts that grow out from the tree trunk and have leaves, flowers or fruit growing on them |
|
deciduous |
a tree that loses its leaves in the autumn every year |
|
evergreen |
a tree or bush which has given leaves all the year round |
|
fruit |
something which grows on a tree/bush and which contains seeds or a stone covered by a substance that you can eat |
|
petal |
thin coloured or white parts which form part of the flower |
YEAR 2
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 2
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Materials (Uses of everyday materials) |
|
|
material |
any substance that has a name, for example paper, wood, iron, air, water. Everything is made up of material |
|
squash |
pressed or crushed with such force that something loses its shape |
|
bend |
to bend into a curved shape |
|
twist |
turn something to make a spiral shape |
|
stretch |
to change the shape by pulling a material |
|
solid |
a solid can hold its shape, for example water in solid form is ice |
|
shape |
the shape of an object is its outline |
|
change |
to make or become different |
|
purpose |
the job that a particular material is used for |
|
property |
the quality or feature that belongs to something and makes it recognisable |
|
Electricity (Lighthouses) |
|
|
electricity |
a form of energy that can be carried by wires and is used for heating and lighting, and to provide power for devices |
|
appliance |
a machine in your home that you use to do a job such as cleaning or cooking. Appliances are often electrical |
|
circuit |
a complete path that electricity flows around |
|
cell |
the power source of a circuit |
|
wire |
long thin piece of metal used to carry electricity around a circuit |
|
bulb |
the part of a lamp that gives out light |
|
break |
a gap in the circuit |
|
complete |
a circuit with no gaps |
|
crocodile clip |
a metal object with sharp teeth that is shaped like a crocodile’s head and is used for connecting an electrical cable to something such as a battery |
|
Animals including Humans |
|
|
exercise |
when you exercise, you move your body energetically in order to get fit and remain healthy |
|
diet |
the kinds of food that a person, animal or community eats |
|
food groups |
there are five basic food groups: fruit and vegetables; starchy food; dairy; proteins and fats |
|
survive |
to continue to exist |
|
hygiene |
it is how we stay clean to prevent illness |
|
growth |
the process of increasing in size |
|
healthy |
well and not suffering from any illness |
|
unhealthy |
not having good health |
|
Plants |
|
|
seeds |
a small, hard part from which a new plant grows |
|
bulbs |
a root shaped like an onion that grows into a flower or plant |
|
shoot |
is the whole stem, together with all the parts that are attached to it, such as a leaf or flower |
|
Living Things and their Habitats |
|
|
mountain |
areas of land that are much higher than the land surrounding them |
|
desert |
places that don’t get main rain and are very dry |
|
rainforest |
an area full of tall trees and leafy plants that gets a lot of rain |
|
savannah |
an area covered with tall grasses |
|
habitat |
places where animals and plants live |
|
food chain |
how energy is passed between plants and animals |
|
polar |
polar habitats are located at the very top and very bottom of the earth. They are cold, windy and have lots of snow and ice. |
|
ocean |
an area which covers much of earth with salt water |
|
micro-habitat |
a very specific, small home environment for plants, animals and insects |
YEAR 3
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 3
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Rocks |
|
|
fossil |
a trace or print or the remains of a plant or animal of a past age preserved in earth or rock |
|
soil |
the substance on the surface of the earth in which plants grow |
|
igneous |
rocks that are formed by volcanic action or intense heat |
|
sedimentary |
are rocks formed from sediment. They are deposited over time, and often show layers which can be seen in cliffs |
|
metamorphic |
rocks that have had their original structure changed by pressure and heat |
|
permeable |
if a substance is permeable, something such as water or gas can pass through it or soak into it |
|
rock |
the hard substance which the earth is made up of |
|
deposit |
layer of solid material, left or laid down by a natural process |
|
crystals |
a special kind of solid material formed when liquids cool and start to harden. They fit together in a repeating pattern |
|
grains |
a grain of something such as sand or salt is a tiny hard piece of it |
|
Forces and Magnets |
|
|
attract |
if one object attracts another object, it causes the second object to move towards it |
|
repel |
to force something to move away or apart |
|
poles |
the ends of a magnet are called poles – N or S |
|
magnetic |
An object that produces a magnetic force called a magnetic field |
|
friction |
the resistance of motion where there is contact between two surfaces |
|
resistance |
a force which slows down a moving object or vehicle |
|
Light |
|
|
translucent |
if a material is translucent, some light can pass through it |
|
transparent |
if an object or substance is transparent, you can see through it clearly |
|
opaque |
if an object or substance is opaque, you cannot see through it |
|
reflect |
sent back from the surface and not pass through it |
|
shadow |
a dark shape on a surface that is made when something stands between a light and the surface |
|
dark |
the absence of light |
|
light source |
where the light comes from |
|
Animals including humans |
|
|
skeleton |
the framework of bones in your body |
|
muscle |
tissue in the body of animals and humans that moves parts of the body |
|
contract |
to make smaller by drawing together; shrink or make tighter |
|
support |
to hold something up |
|
protection |
the act of protecting or the state of being protected, preservation from injury or harm |
|
movement |
the act or process of moving people or things from one place or position to another |
|
nutrition |
the process of taking food into the body and absorbing the nutrients in those foods |
|
carbohydrate |
is a nutrient that gives you energy, for example bread, potatoes and pasta. |
|
protein |
is a nutrient that helps your body to grow and repair itself, for example red meat, yoghurt, beans. |
|
dairy |
any foods made from milk products of animals |
|
vitamins |
are substances found in foods that our bodies need to work and be healthy, eg Vitamin C found in fruit |
|
minerals |
help your body grow, develop, and stay healthy, such as calcium found in milk |
|
fat |
is a nutrient that gives you energy and is found in nuts, oils and avocadoes |
|
Plants |
|
|
nutrients |
substances that help plants and animals to grow |
|
germinate |
if a seed germinates, it starts to grow |
|
pollinate |
to pollinate a plant or tree means to fertilise it with pollen. This is often done by insects |
|
disperse |
to scatter, separate or spread through a large area |
|
dispersal |
is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant |
YEAR 4
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 4
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Materials (States of Matter) |
|
|
volume |
the space that a substance (solid, liquid, gas, or plasma) or shape occupies or contains |
|
capacity |
the maximum amount that something can hold – usually ml or l |
|
particles |
a tiny amount or small piece of matter |
|
solid |
having a firm shape or form that can be measured in length, width and height not like a liquid or a gas |
|
liquid |
in a form that flows easily and is neither a solid nor a gas |
|
gas |
a form of matter that is neither liquid nor solid. A gas rapidly spreads out when it is warmed and contracts when it is cooled |
|
melt |
to change from a solid to a liquid state through heat or pressure |
|
freeze |
where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point |
|
evaporate |
to turn from liquid into gas, pass away in the form of vapour |
|
condense |
change or cause to change from a gas or vapour to a liquid |
|
precipitation |
rain, snow, sleet, drew etc. formed by condensation of water vapour in the atmosphere |
|
Electricity |
|
|
component |
Part of an electrical circuit |
|
buzzer |
an electrical device that is used to make a buzzing sound |
|
lamp |
a device for giving light |
|
switch |
a small control for an electrical device which you use to turn the device on or off |
|
conductor |
a substance that heat or electricity can pass through or along |
|
insulator |
a non-conductor of electricity or heat |
|
Sound |
|
|
pitch |
the quality of a sound that allows you to label it as “higher” or “lower” to your ear |
|
vibrate |
move continuously and rapidly to and fro |
|
sound insulation |
is the ability of building elements or structure to reduce sound transmission |
|
source |
where something comes from |
|
decibel |
a unit of measure of how loud a sound is - dB |
|
sound waves |
invisible waves that travel through air, water and objects as vibrations |
|
Animals including Humans (Teeth and Digestion) |
|
|
digestion |
breaking down ingested food material |
|
saliva |
the watery liquid that forms in your mouth and helps you to chew and digest food |
|
incisors |
the teeth at the front of your mouth which you use for biting into food |
|
canines |
pointed teeth near the front of the mouth of humans and of some animals |
|
pre-molars |
two situated on each side of both jaws between the first molar and the canine |
|
molars |
the large, flat teeth towards the back of your mouth that you use for chewing food |
|
oesophagus |
the part of your body that carries the food from the throat to the stomach |
|
intestine |
the tubes in your body through which food passes when it has left your stomach |
|
rectum |
final section of the large intestine, finishing at the anus |
|
anus |
opening where your bowel movements come out |
|
producer |
organisms that make their own food using energy from the sun |
|
consumer |
organisms that are unable to make their own energy, and instead rely on the consumption and digestion of producers or another consumer, or both to survive. |
|
predator |
an animal that kills and eats other animals |
|
prey |
an animal hunted or captured by another for food |
|
invertebrate |
a creature that does not have a spine, for example an insect, a worm or an octopus |
|
Living Things and their Habitats |
|
|
movement |
an act of moving |
|
sensitivity |
responding to the external environment |
|
reproduction |
when an animal or plant produces one or more individuals similar to itself |
|
excretion |
the process of eliminating waste produced from their metabolisms from the body |
|
respiration |
a chemical reaction that occurs in all living cells where energy is released form glucose |
|
growth |
an increase in something |
|
environment |
the external surroundings that affect the survival and development of an organism or population |
|
mammal |
is an animal that breaths air, has a backbone and grows hair at some point in their life |
YEAR 5
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 5
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Materials (Properties and changes of materials) |
|
|
separate |
divide into constituent or distinct elements |
|
filter |
the removal of dirt or other solids from liquids or gases |
|
reversible |
able to turn or change back |
|
irreversible |
impossible to reverse, turn back or change |
|
soluble |
able to dissolve |
|
insoluble |
impossible to dissolve, especially in a given liquid |
|
dissolve |
To seem to disappear by being distributed in a liquid (solvent) |
|
solution |
a mixture that contains two to more substances combined evenly |
|
solvent |
able to dissolve other substances |
|
Forces |
|
|
gravity |
the force which causes things to drop to the ground |
|
weight |
is the name of the force exerted on an object due to the acceleration of gravity |
|
mass |
Is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg) |
|
gravitational pull |
is the attraction that Earth exerts on an object or the object exerts on the Earth |
|
air resistance |
Is the opposing force to the motion of an object in air or water |
|
water resistance |
is the friction that is created between water and an object this is moving through it |
|
streamlined |
a streamlined vehicle, animal or object has a shape that allows it to move quickly or efficiently through air or water |
|
pulley |
a simple machine that makes lifting something easier. A pulley has a wheel or set of wheels with groves that a rope or chain can be pulled over |
|
gear |
a part of a machine that causes another part to move because of teeth which connect the two moving parts |
|
lever |
a basic tool used to lift or pry things open |
|
Earth and Space |
|
|
Earth |
is the third planet from the Sun |
|
sun |
is the star at the centre of our solar system |
|
moon |
a celestial body that orbits a planet |
|
orbit |
is a regular, repeating path that one object in space takes around another one |
|
planet |
a large, round object in space that moves around a star |
|
star |
a large ball of burning gas in space |
|
day – length |
the time between sunrise and sunset, i.e. the duration of daylight |
|
night – length |
the period of darkness from sunset to sunrise in each twenty four hours, when the sun is below the horizon |
|
solar system |
consists of the sun and everything that orbits, or travels around, the sun. |
|
rotate |
move or cause to move in a circle round an axis or centre |
|
year |
the time taken by a planetary body to orbit the sun |
|
universe |
the whole of space and all the stars, planets and other forms of matter and energy in it |
|
galaxy |
the extremely large group of stars and planets. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way |
|
satellite |
is a moon, planet or machine that orbits a planet or a star. Usually the word satellite refers to a machine that is launched into space and moves around earth or another body in space |
|
heliocentric |
having the sun at its centre – the accepted model of the solar system |
|
spherical |
an object shaped like a round ball |
|
mercury |
is the smallest and innermost planet in the solar system |
|
venus |
the second planet from the sun |
|
mars |
the planet fourth in order from the sun and known for its red colour |
|
Light |
|
|
dim |
light that is not bright |
|
emit |
to emit a sound or light means to produce it |
|
Light ray |
A path along which light follows |
|
Straight Lines |
the direction of travel that a light ray takes |
|
celestial |
pertaining to the sky or visible heaven, or to the universe |
|
Animals including Humans (Changes, Life Cycles) |
|
|
puberty |
the stage in someone’s life when their body starts to become physically mature |
|
penis |
the male organ for reproduction by which urine and semen are discharged from the body |
|
testes |
male reproductive gland that produces sperm and secretes testosterone and is contained within the scrotum |
|
sperm |
the male reproductive cell |
|
urethra |
the tube through which urine leaves the body. It empties urine from the bladder |
|
fallopian tube |
one of two long slender tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. Eggs pass from the ovaries, through the fallopian tubes, to the uterus |
|
gestation |
foetal development period from the time of conception until birth. In humans, the full gestation period is normally nine months |
|
foetus |
unborn offspring of a mammal at the later stages of its development, especially a human from eight weeks after fertilisation to its birth |
|
egg |
the female reproductive cell |
|
uterus |
the organ in the lower body of a woman or female mammal where offspring are conceived and in which they gestate before birth, the womb |
|
menstruation |
the approximately monthly discharge of blood from non-pregnant women from puberty to the menopause |
|
Plants (Life Cycles) |
|
|
stigma |
the top of the centre part of the flower which takes in pollen |
|
stamen |
the male reproductive part of a flower. The stamen consists of a long slender stalk, the filament with a two-lobed anther at the top. |
|
pollen |
a fine powder produced. It fertilises other flowers of the same species so that they produce seeds |
|
filament |
the stalk of the stamen |
|
ovary |
a female organ that produces eggs |
|
pollination |
to pollinate a plant or tree means to fertilise it with pollen. This is often done by insects |
|
anther |
the part of the stamen that produces and releases the pollen |
|
style |
a long, slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary. The stigma is at the top of the style, and is a sticky platform where pollen is deposited |
|
ovule |
is the part that contains the female reproductive cells |
|
Living things and their habitats |
|
|
metamorphosis |
is a process that some animals go through to become adults. It is common in insects. |
|
Sexual reproduction |
A type of reproduction where new individuals come from both a male and female parent |
|
Asexual reproduction |
a type of reproduction where new individuals come from a single organism/parent |
|
tadpole |
Is the larval stage of an amphibian |
|
froglet |
a young frog, one that has recently metamorphosed from a tadpole |
|
frogspawn |
is a soft substance like jelly which contains the eggs of a frog |
|
chrysalis |
is a butterfly or moth in the stage between being a larva and an adult |
|
pupa |
an insect in a middle stage of its development. Pupas do not eat or move, they are changing into their adult form |
|
cocoon |
is a covering or case made by some animals to protect themselves or their young as they develop into adults |
|
nymph |
the young stage of insects |
YEAR 6
Science vocabulary and definitions
Year 6
|
Biology |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Electricity |
|
|
Voltage (KS3) |
the force of an electric current as measured in volts |
|
Resistance (KS3) |
a force which slows down a moving object or vehicle |
|
current |
a flow of electricity through a wire or circuit |
|
Living Things and their Habitats |
|
|
classify |
to group living things based on their characteristics |
|
characteristic |
the qualities or features that belong to them and make them recognisable |
|
vertebrate |
Animal that has an internal skeleton of bone or cartilage |
|
invertebrate |
a creature that does not have an internal vertebral column insect, a worm or an octopus |
|
microorganism |
An organism too small to be seen with the naked eye eg bacteria or algae |
|
divide |
to separate into two or more parts |
|
sub-divide |
to divide (that which has already been divided) into smaller parts |
|
Evolution and Inheritance |
|
|
adapt |
become adjusted to new conditions |
|
ancestor |
an early type of animal or plant from which a later, usually dissimilar type has evolved |
|
biodiversity |
a wide variety of plant and animal species living in their natural environment |
|
biome |
a large naturally occurring community of animals and plants occupying a major habitat |
|
Breed (verb) |
to produce plants or animals by reproduction |
|
characteristic |
the qualities or features that belong to them and make them recognisable |
|
descendant |
those in a descending line of birth from an individual |
|
extinct |
no longer has any living members, either in the world or in a particular place |
|
generation |
the act or process of bringing into being, through reproduction, especially of off spring |
|
maladaptation |
the failure to adapt properly to a new situation or environment |
|
natural selection |
a process by which species of animals and plants that are best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce, while those that are less well adapted die out |
|
offspring |
a person’s children or an animal’s young |
|
variation |
a change or slight difference |
|
mutate |
change in the genetic code |
|
inherit |
A characteristic passed on from parents to their offspring |
|
evolve |
the change in the characteristics of a species over several generations, relying on the process of natural selection |
|
species |
a class of plants or animals whose members have the same main characteristics and are able to breed with each other |
|
survive |
continue to exist |
|
reproduce |
to produce one or more individuals similar to itself |
|
Animals including Humans (Circulatory System) |
|
|
heart |
the organ in your chest that pumps the blood around your body |
|
artery |
blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from your heart to the rest of your body |
|
vein |
a tube in your body that carries deoxygenated blood to your heart from the rest of your body |
|
capillary |
tiny blood vessel |
|
ventricle |
a chamber of the heart, having thick muscular walls that receives blood from atrium and pumps it to the arteries |
|
lungs |
two organs inside your chest which fill with air when you breathe in. They oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide from it |
|
blood vessels |
the narrow tubes through which your blood flows. Arteries, veins and capillaries are blood vessels. |
|
pulse |
the regular beating of blood through your body. |
|
oxygen |
a colourless gas that plants and animals need to survive |
|
de-oxygenated |
blood that does not contain oxygen |
|
oxygenated |
blood that contains oxygen |
|
atrium |
a chamber of the heart that receives blood from the veins and forces it into a ventricle or ventricles |
|
valve |
controls blood flow to and from the heart. There are four valves in the heart |
|
circulatory system |
the system responsible for circulating blood through the body, that supplies nutrients and oxygen to the body and removes waste products such as carbon dioxide |